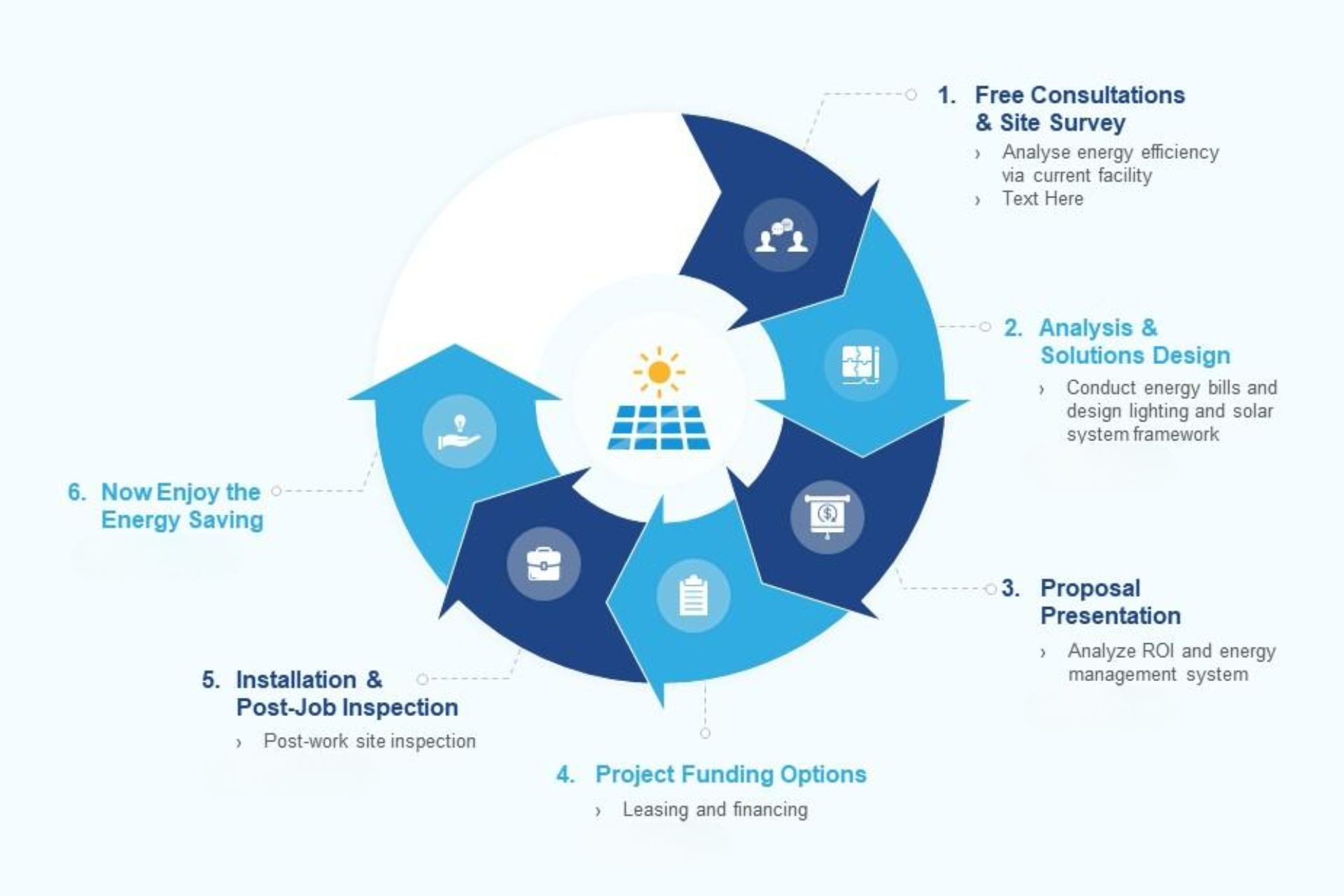
It’s a simple process that only requires getting a utility bill to get started.
Learn about
The 9 Steps to Going Solar
1) Solar Proposal
2) Financing Approval
3) Site Survey
4) Engineering
5) Permitting
6) Installation
7) Inspections
8) Utility Connect
9) Activation
1. Solar Proposal
A solar proposal typically includes detailed information about the proposed solar energy system, including:
- Project Overview: A brief summary of the project, its objectives, and the proposed solar energy system.
- System Design: A detailed description of the solar energy system’s design, including the number of panels, their placement, and the type of inverters and batteries to be used.
- Energy Production: A calculation of the expected energy production of the solar energy system, including annual and monthly estimates.
- Cost Estimate: A breakdown of the costs associated with the solar energy system, including equipment, installation, and maintenance costs.
- Financing Options: A discussion of the available financing options for the project, including purchase, lease, and power purchase agreements.
- Return on Investment: A calculation of the expected return on investment for the solar energy system, including payback period and projected savings.
- Environmental Impact: An assessment of the environmental impact of the solar energy system, including its carbon footprint and other environmental benefits.
- Project Timeline: A timeline for the installation and commissioning of the solar energy system.
- Warranty and Maintenance: Details of the warranty and maintenance services that will be provided for the solar energy system.
Overall, a solar proposal provides a comprehensive overview of the proposed solar energy system and its benefits, costs, and environmental impact, to help the client make an informed decision.
Project Overview
System Design
energy production
cost estimate
financing options
return on investment
environmental impact
project timeline
warranty and maintenance
2. Financing Approval
Financing approval for a solar loan typically requires the following information:
- Credit Score: Your credit score is a critical factor in determining your eligibility for a solar loan. A higher credit score usually means a better chance of approval and more favorable loan terms.
- Income and Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lenders will look at your income to determine whether you can afford the loan payments, and your debt-to-income ratio to assess your overall financial health.
- Employment Status: Lenders will want to know your employment status and length of employment to determine your financial stability.
- Collateral: Some lenders may require collateral, such as the solar panels themselves or other assets, to secure the loan.
- Loan Amount and Terms: You will need to specify the loan amount and the loan term you are seeking. Longer terms will generally result in lower monthly payments but may also result in higher interest charges over the life of the loan.
- Type of Solar System: The lender may want to know details about the type of solar system you plan to install, including the size, cost, and expected energy savings.
- Documentation: You will likely need to provide documentation, such as proof of income, tax returns, and proof of homeownership.
Once you provide all of the necessary information, the lender will review your application and make a decision on whether to approve the loan. If approved, you will receive the loan funds, and you can proceed with the installation of your solar system.
Credit Score Minimum 620
Income
Employment
Loan Amount and Terms
property type
income documentation
3. Site Survey
A residential solar site survey is a detailed inspection of a property to assess its suitability for a solar energy system installation. The survey typically includes the following components:
- Shading Analysis: A shading analysis is conducted to determine how much sunlight the property receives throughout the day and to identify any potential shading issues that could affect the performance of the solar panels.
- Roof Inspection: The surveyor will inspect the roof to assess its condition, orientation, and slope. They will also determine the available roof space for solar panel installation and evaluate the roof’s structural integrity.
- Electrical Assessment: The surveyor will evaluate the electrical system to determine if it can support the additional load of a solar energy system.
- Energy Usage Analysis: The surveyor will review the homeowner’s electricity bills to determine the property’s energy usage patterns, which will help determine the appropriate size of the solar energy system.
- Local Building Codes and Permits: The surveyor will review local building codes and permit requirements to ensure that the proposed solar energy system installation meets all regulations.
- Site Photos and Measurements: The surveyor will take photos of the property and measure the available roof space to assist with the system design and engineering process.
Overall, a residential solar site survey is a critical step in the solar energy system installation process as it provides the necessary information to ensure that the solar energy system is designed and installed to maximize energy production and efficiency.
Shading Analysis
Roof Inspection
Electrical Assessment
Energy usage analysis
local building codes and permits
site photos and measurements
4. Engineering
When a solar project is sent to engineers, the engineering team will evaluate the proposed solar energy system’s design and ensure that it is safe, efficient, and meets all applicable codes and standards. This process typically involves the following steps:
- System Design Review: The engineering team will review the solar energy system’s design and evaluate its feasibility, including the system’s sizing, layout, and equipment specifications.
- Structural Analysis: The engineering team will conduct a structural analysis to ensure that the solar energy system can be safely installed on the property’s roof or ground, taking into account any environmental factors such as wind, snow, or seismic loads.
- Electrical Design and Analysis: The engineering team will review the electrical design of the solar energy system to ensure that it meets all applicable electrical codes and standards, and can safely connect to the existing electrical grid.
- Equipment Selection and Evaluation: The engineering team will evaluate the equipment to be used in the solar energy system, including solar panels, inverters, and batteries, to ensure that they are of high quality, meet industry standards, and are compatible with the proposed system design.
- System Performance Modeling: The engineering team will use specialized software to model the solar energy system’s performance, taking into account factors such as shading, climate, and location, to ensure that the proposed system will meet the expected energy production targets.
- Permitting and Compliance: The engineering team will ensure that the solar energy system design and installation comply with all local, state, and federal regulations, and assist with the permitting process if necessary.
Once the engineering review is complete, the solar contractor will receive a report detailing any recommended changes or adjustments to the solar energy system design. The solar contractor will then work with the homeowner to finalize the system design and obtain any necessary approvals, such as building permits or utility interconnection agreements, before proceeding with the installation.
System Design review
structural analysis
electrical design and analysis
equipment selection and evaluation
system performance modeling
permitting and compliance
5. Permitting
The permitting process for a residential solar energy system installation can vary depending on the location, but generally includes the following steps:
- Researching Local Requirements: The solar contractor will research the local requirements for solar energy system installations, which can include building codes, zoning regulations, and electrical permits.
- Completing the Application: The solar contractor will complete the permit application, which typically includes details about the solar energy system’s design, including the system’s size, equipment specifications, and installation location.
- Submitting the Application: The solar contractor will submit the permit application to the local permitting office, which may include the building department, planning department, or other relevant agencies.
- Review and Approval: The local permitting office will review the permit application and either approve or request modifications to the solar energy system’s design. Depending on the location, this process can take several weeks to several months.
- Permit Issuance: Once the permit is approved, the solar contractor will receive the permit, allowing them to begin the solar energy system installation.
- Inspection: After the solar energy system installation is complete, the local permitting office will conduct an inspection to ensure that the system was installed according to the approved permit and meets all applicable codes and standards.
- Final Approval: After passing the inspection, the local permitting office will issue a final approval, allowing the solar energy system to be connected to the electrical grid and start generating electricity.
It is essential to comply with all local permitting requirements as failure to do so may result in fines or the need to remove the solar energy system. Working with an experienced solar contractor can help ensure that the permitting process is completed accurately and efficiently.
Researching Local Requirements
Completing the Application
Submitting the Application
Review and Approval
Permit Issuance
Inspection
Final Approval
6. Installation
The installation process for residential solar energy systems typically involves the following steps:
- Pre-Installation: Before installation, the solar contractor will confirm the system design, obtain any necessary permits, and coordinate with the homeowner to schedule the installation.
- Equipment Delivery: The solar contractor will deliver the solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and other equipment to the installation site.
- Installation of Mounting Hardware: The solar contractor will install the mounting hardware, which may include roof or ground mounts, to secure the solar panels to the property.
- Wiring: The solar contractor will run the wiring from the solar panels to the inverter and connect the inverter to the property’s electrical system.
- Panel Installation: The solar contractor will install the solar panels onto the mounting hardware, positioning them to maximize solar exposure and energy production.
- Electrical Inspection: After the solar panels are installed and wired, the electrical inspector will verify that the system is wired correctly and meets all electrical codes.
- Grid Connection: Once the system passes the electrical inspection, the solar contractor will coordinate with the local utility to connect the solar energy system to the electrical grid.
- System Testing: The solar contractor will test the system to ensure that it is generating electricity correctly and meeting the expected energy production targets.
- Customer Orientation: The solar contractor will provide the homeowner with a comprehensive orientation, explaining how the system works, how to monitor system performance, and any maintenance requirements.
Overall, the installation process for a residential solar energy system typically takes between one to three days, depending on the system’s size and complexity. However, larger systems may require more installation time. It is essential to work with a reputable solar contractor who has experience with residential solar installations to ensure that the installation is completed safely and efficiently.
Pre-Installation
Equipment Delivery
Installation of Mounting Hardware
Wiring
Panel Installation
Electrical Inspection
Grid Connection
System Testing
Customer Orientation
7. Inspections
The inspection process for a residential solar energy system typically involves the following steps:
- Pre-Inspection: Before the inspection, the solar contractor will ensure that the solar energy system is fully installed and operational, and that all necessary permits have been obtained.
- Electrical Inspection: The electrical inspector will verify that the solar energy system is wired correctly and meets all applicable electrical codes and standards. This inspection will typically involve checking the wiring, grounding, and disconnects, as well as verifying that the system’s voltage and current levels are within the acceptable range.
- Structural Inspection: The structural inspector will evaluate the installation’s structural integrity to ensure that it meets all applicable building codes and standards. This inspection may involve checking the mounting hardware, roof or ground supports, and any other components of the solar energy system that may affect the property’s structural integrity.
- Building Inspection: The building inspector will verify that the solar energy system’s installation complies with all applicable building codes and standards, including any zoning or permitting requirements. This inspection may involve checking the system’s height, location, and setbacks from property lines or other structures.
- Interconnection Inspection: If the solar energy system is connected to the electrical grid, the local utility will conduct an interconnection inspection to ensure that the system is connected correctly and meets all utility interconnection requirements.
Once the inspection is complete, the inspector will provide a report detailing any deficiencies or issues that need to be addressed. The solar contractor will then work to address these issues and ensure that the solar energy system meets all applicable codes and standards. Once any deficiencies are corrected, the inspector will issue a final approval, allowing the solar energy system to be connected to the electrical grid and start generating electricity.
Pre-Inspection
Electrical Inspection
Structural Inspection
Building Inspection
Interconnection Inspection
8. Utility Connect
The utility connection for a residential solar energy system typically involves the following steps:
- Application: The solar contractor will submit an interconnection application to the local utility, requesting to connect the solar energy system to the electrical grid.
- Approval: The utility will review the interconnection application and approve it if the system meets all interconnection requirements. This process may take several weeks or months, depending on the utility and the location.
- Installation: Once the solar energy system is installed and passes all required inspections, the solar contractor will coordinate with the utility to connect the system to the electrical grid.
- Meter Installation: The utility will install a net meter, which measures the electricity that the solar energy system generates and the electricity that the homeowner consumes from the grid. This meter will allow the homeowner to receive credits for any excess electricity generated by the solar energy system.
- Permission to Operate: After the meter installation, the utility will conduct a final inspection to ensure that the solar energy system is connected correctly and meets all utility interconnection requirements. Once the system passes this inspection, the utility will grant permission to operate, allowing the homeowner to start generating electricity from the solar energy system.
It is important to note that the utility connection process can vary depending on the utility and the location. Working with a reputable solar contractor who has experience with the local interconnection process can help ensure that the utility connection is completed efficiently and correctly.
Application
Approval
Installation
Meter Installation
Permission to Operate
9. Activation
The activation of a residential solar energy system typically involves the following steps:
- System Testing: The solar contractor will test the system to ensure that it is generating electricity correctly and meeting the expected energy production targets. This testing will involve checking the system’s voltage, current, and power output, as well as verifying that all components are working correctly.
- Monitoring Setup: The solar contractor will set up a monitoring system that allows the homeowner to track the system’s performance and energy production. This may involve setting up a web-based monitoring system that the homeowner can access through a computer or mobile device.
- Utility Notification: Once the solar energy system is generating electricity, the solar contractor will notify the utility that the system is operational and connected to the electrical grid.
- Permission to Operate: The utility will conduct a final inspection to ensure that the solar energy system is connected correctly and meets all utility interconnection requirements. Once the system passes this inspection, the utility will grant permission to operate, allowing the homeowner to start generating electricity from the solar energy system.
- Net Metering Setup: The utility will install a net meter, which measures the electricity that the solar energy system generates and the electricity that the homeowner consumes from the grid. This meter will allow the homeowner to receive credits for any excess electricity generated by the solar energy system.
- Customer Orientation: The solar contractor will provide the homeowner with a comprehensive orientation, explaining how the system works, how to monitor system performance, and any maintenance requirements.
- Mobile App
Overall, the activation process for a residential solar energy system typically takes a few days to a few weeks, depending on the utility and the location. It is essential to work with a reputable solar contractor who has experience with residential solar installations to ensure that the activation process is completed safely and efficiently.
System Testing
Monitoring Setup
Utility Notification
Permission to Operate
Net Metering Setup
Customer Orientation
Overview
These are the steps involved in the residential solar process to help you gain a better insight and education yourself and others on how solar works.